You can use the Azure CLI to create and manage Azure resources from the command line or in scripts. This quickstart describes how to use the Azure CLI to create an Azure Database for MariaDB server in an Azure resource group in about five minutes.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. .
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
- This article requires version 2.0 or later of the Azure CLI. If using Azure Cloud Shell, the latest version is already installed.
If you have multiple subscriptions, choose the subscription that contains the resource or the subscription in which you are billed. To select a specific subscription ID in your account, use the az account set command:
Azure CLI
az account set --subscription 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
Create a resource group
Create an Azure resource group by using the az group create command. A resource group is a logical container in which Azure resources are deployed and managed as a group.
The following example creates a resource group named myresourcegroup in the westus location:
Azure CLI
az group create --name myresourcegroup --location westus
Create an Azure Database for MariaDB server
Create an Azure Database for MariaDB server by using the az mariadb server create command. A server can manage multiple databases. Typically, a separate database is used for each project or for each user.
| Setting | Sample value | Description |
| name | mydemoserver | Enter a unique name that identifies your Azure Database for MariaDB server. The server name can contain only lowercase letters, numbers, and the hyphen (-) character. It must contain between 3 and 63 characters. |
| resource-group | myresourcegroup | Enter the name of the Azure resource group. |
| sku-name | GP_Gen5_2 | The name of the SKU. Follows the convention pricing tier_compute generation_vCores in shorthand. For more information about the sku-name parameter, see the section after this table. |
| backup-retention | 7 | How long a backup should be retained. The unit is days. Range: 7 to 35. |
| geo-redundant-backup | Disabled | Whether geo-redundant backups should be enabled for this server. Allowed values: Enabled, Disabled. |
| location | westus | The Azure location for the server. |
| ssl-enforcement | Enabled | Whether SSL should be enabled for this server. Allowed values: Enabled, Disabled. |
| storage-size | 51200 | The storage capacity of the server (the unit is megabytes). Valid storage sizes are 5,120 MB (minimum) with increases in 1,024-MB increments. For more information about storage size limits, see Pricing tiers. |
| version | 10.2 | The MariaDB major engine version. |
| admin-user | myadmin | The user name for the administrator login. The admin-user parameter can't be azure_superuser, admin, administrator, root, guest, or public. |
| admin-password | your password | The password of the administrator user. Your password must contain between 8 and 128 characters. It must contain characters from three of the following categories: English uppercase letters, English lowercase letters, numbers, and non-alphanumeric characters. |
The sku-name parameter value follows the convention {pricing tier}_{compute generation}_{vCores} as in the examples below:
--sku-name B_Gen5_1maps to Basic, Gen 5, and 1 vCore. This option is the smallest SKU available.--sku-name GP_Gen5_32maps to General Purpose, Gen 5, and 32 vCores.--sku-name MO_Gen5_2maps to Memory Optimized, Gen 5, and 2 vCores.
For information about valid values by region and for tiers, see Pricing tiers.
The following example creates a server named mydemoserver in the West US region. The server is in the resource group myresourcegroup and has the server admin login myadmin. The server is a Gen 5 server in the General Purpose pricing tier and it has 2 vCores. A server name maps to a DNS name and must be globally unique in Azure. Substitute <server_admin_password> with your own server admin password.
Azure CLI
az mariadb server create --resource-group myresourcegroup --name mydemoserver --location westus --admin-user myadmin --admin-password <server_admin_password> --sku-name GP_Gen5_2 --version 10.2
Note
Consider using the Basic pricing tier if light compute and I/O are adequate for your workload. Note that servers created in the Basic pricing tier cannot later be scaled to General Purpose or Memory Optimized. See the pricing page for more information.
Configure a firewall rule
Create an Azure Database for MariaDB server-level firewall rule by using the az mariadb server firewall-rule create command. A server-level firewall rule allows an external application like the mysql command-line tool or MySQL Workbench to connect to your server through the Azure Database for MariaDB service firewall.
The following example creates a firewall rule called AllowMyIP that allows connections from a specific IP address, 192.168.0.1. Substitute an IP address or range of IP addresses that corresponds to the location you connect from.
Azure CLI
az mariadb server firewall-rule create --resource-group myresourcegroup --server mydemoserver --name AllowMyIP --start-ip-address 192.168.0.1 --end-ip-address 192.168.0.1
Note
Connections to Azure Database for MariaDB communicate over port 3306. If you try to connect from inside a corporate network, outbound traffic over port 3306 might not be allowed. In this case, you can connect to your server only if your IT department opens port 3306.
Configure SSL settings
By default, SSL connections between your server and client applications are enforced. This default setting ensures security of "in-motion" data by encrypting the data stream over the internet. For this quickstart, disable SSL connections for your server. Disabling SSL is not recommended for production servers. The following example disables SSL enforcing on your Azure Database for MariaDB server:
Azure CLI
az mariadb server update --resource-group myresourcegroup --name mydemoserver --ssl-enforcement Disabled
Get connection information
To connect to your server, you need to provide host information and access credentials. To get the connection information, run the following command:
Azure CLI
az mariadb server show --resource-group myresourcegroup --name mydemoserver
The result is in JSON format. Make a note of the values for fullyQualifiedDomainName and administratorLogin.
JSONCopy
{
"administratorLogin": "myadmin",
"earliestRestoreDate": null,
"fullyQualifiedDomainName": "mydemoserver.mariadb.database.azure.com",
"id": "/subscriptions/00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000/resourceGroups/myresourcegroup/providers/Microsoft.DBforMariaDB/servers/mydemoserver",
"location": "westus",
"name": "mydemoserver",
"resourceGroup": "myresourcegroup",
"sku": {
"capacity": 2,
"family": "Gen5",
"name": "GP_Gen5_2",
"size": null,
"tier": "GeneralPurpose"
},
"sslEnforcement": "Enabled",
"storageProfile": {
"backupRetentionDays": 7,
"geoRedundantBackup": "Disabled",
"storageMb": 5120
},
"tags": null,
"type": "Microsoft.DBforMariaDB/servers",
"userVisibleState": "Ready",
"version": "10.2"
}
Connect to the server by using the mysql command-line tool
Connect to your server by using the mysql command-line tool. You can download the command-line tool and install it on your computer. You can also access the command-line tool by selecting the Try It button on a code sample in this article. Another way to access the command-line tool is to select the \>_ button on the upper-right toolbar in the Azure portal to open Azure Cloud Shell.
To connect to the server by using the mysql command-line tool:
Connect to the server:
Azure CLI
mysql -h mydemoserver.mariadb.database.azure.com -u myadmin@mydemoserver -pView the server status at the
mysql>prompt:SQLCopy
statusYou should see something similar to the following text:
Windows Command PromptCopy
C:\Users\>mysql -h mydemoserver.mariadb.database.azure.com -u myadmin@mydemoserver -p Enter password: *********** Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 65512 Server version: 5.6.39.0 MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2016, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. mysql> status -------------- mysql Ver 14.14 Distrib 5.7.23, for Linux (x86_64) Connection id: 64681 Current database: Current user: myadmin@40.118.201.21 SSL: Cipher in use is AES256-SHA Current pager: stdout Using outfile: '' Using delimiter: ; Server version: 5.6.39.0 MariaDB Server Protocol version: 10 Connection: mydemoserver.mariadb.database.azure.com via TCP/IP Server characterset: latin1 Db characterset: latin1 Client characterset: utf8 Conn. characterset: utf8 TCP port: 3306 Uptime: 1 day 3 hours 28 min 50 sec Threads: 10 Questions: 29002 Slow queries: 0 Opens: 33 Flush tables: 3 Open tables: 1 Queries per second avg: 0.293 -------------- mysql>
Connect to the server by using MySQL Workbench
Open MySQL Workbench on your client's computer. If it's not already installed, download and install the application.
In the Setup New Connection dialog box, on the Parameters tab, enter the following information:
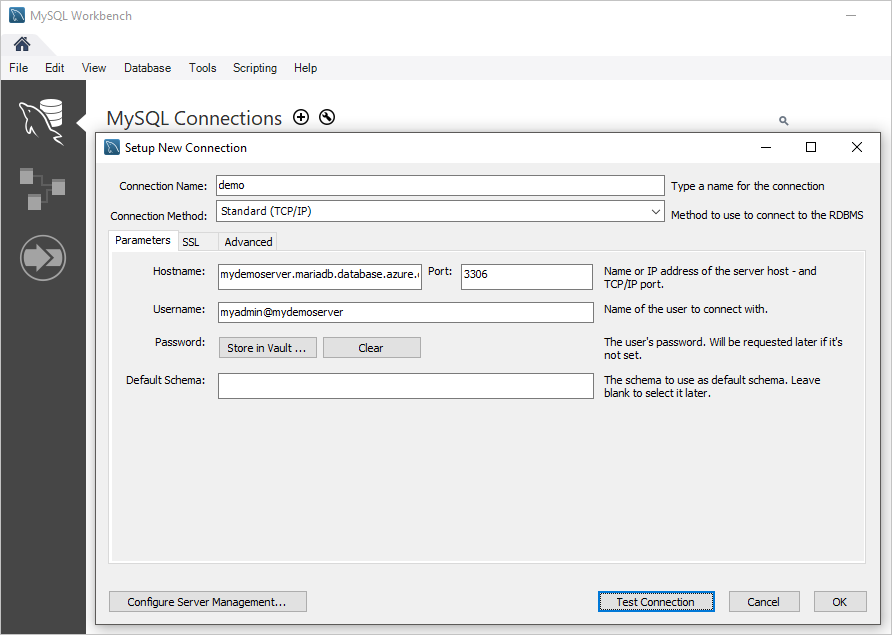
| Setting | Suggested value | Description | | --- | --- | --- | | Connection Name | Demo connection | Enter a label for this connection (the connection name can be anything) | | Connection Method | Standard (TCP/IP) | Use the TCP/IP protocol to connect to Azure Database for MariaDB | | Hostname | mydemoserver.mariadb.database.azure.com | The server name that you noted earlier. | | Port | 3306 | The default port for Azure Database for MariaDB. | | Username | myadmin@mydemoserver | The server admin login that you noted earlier. | | Password | your password | Use the admin account password that you set up earlier. |
To check whether all parameters are configured correctly, select Test Connection.
Select the connection to successfully connect to the server.
Clean up resources
If you don't need the resources that you used in this quickstart for another quickstart or tutorial, you can delete them by running the following command:
Azure CLI
az group delete --name myresourcegroup
If you want to delete only the server that you created in this quickstart, run the az MariaDB server delete command:
Azure CLI
az mariadb server delete --resource-group myresourcegroup --name mydemoserver
Thanks for reading! Do comment and like.
Follow Gayatri Barhate


